
Patients who undergo knee chondroplasty procedures have a 17-fold increased risk of receiving knee arthroplasty than the general population.

Patients who undergo knee chondroplasty procedures have a 17-fold increased risk of receiving knee arthroplasty than the general population.

New findings comparing 3 decades of newly approved indications show the proportion of new approvals being supported by just 1 pivotal trial has quadrupled.

Despite an apparent and increasing need for osteoporosis treatments, fewer people today are taking the medications both here in the United States and abroad.

The international registry that was created in March to track rheumatology patients who have contracted COVID-19, has released data from the first 110 cases from six continents.

United Rheumatology, a management services organization serving over 645 rheumatologists in 39 states, will host a one-day virtual clinical conference focusing on managing a rheumatology practice through the COVID-19 pandemic.

The negative impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on specialty medical practices may lift by the start of next month, according to a new report issued by the market research company Spherix Global Insights.
The American College of Rheumatology has issued treatment guidance for the care of patients with rheumatic diseases during the COVID-19 pandemic.

Jacquelyn Center, PhD, discuss with HCPLive the findings of her study and factors that increase mortality risk.

The findings provide insight into practice, provide a rubric for future studies, and suggest areas to improve resource use and patient care.

Dapansutrile has substantial potential for further development for the treatment of gout flares and other NLRP3-mediated diseases.

The blinded, placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial will seek to enroll more than 500 adult patients.

A conversation on new AI software which can identify a five-fold greater rate of potential fractures.

Physical therapy for knee osteoarthritis improves pain scores and physical function.

In this Q&A, Randy Q. Cron, M.D., Ph.D., a pediatric rheumatologist at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, discusses the role of rheumatologists in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with COVID-19, particularly those who are critically ill and experiencing a cytokine storm syndrome.

In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the Global Rheumatology Alliance has been created to collect data on how the virus is affecting patients with rheumatic diseases or those who are taking immunosuppressive therapies. The alliance, which includes 300 rheumatologists, scientists and patients from throughout the world, has created a registry for physicians to report COVID-19 cases.

Can a patient with hidradenitis suppurativa develop rheumatoid arthritis? Apparently so, according to researchers writing in JAMA Dermatology this month.

COVID-19 is being treated with treatments designed for rheumatoid arthritis. They have their pros and cons. Learn more in this article.

Doses of secukinumab are clinically safe and beneficial for long-term treatment of psoriatic arthritis.

Shelter-in-place orders have led to a "horrifying surge in domestic violence," says the United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres. The World Health Organization asks that healthcare workers be cognizant of the signs and symptoms of domestic violence in their patients. In today's "Awkward Conversations" column, Dr. Kim Gorgens and Margaret Port cover domestic violence among chronically ill patients.
A new study shows there is little to no clinical benefit in reducing TNFi treatment dosages for patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA).

A comprehensive review of published studies on gut microbiota, immunity and arthritis suggests that having a microbial imbalance may precede the development of spondyloarthritides and osteoarthritis.

Investigators grapple with the viability of using chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine to stop the spread of COVID-19.
A 16-year-old African American girl reports sudden erythema covering her nose, cheeks, and upper back. Can you diagnose this patient?
The rheumatology community has expressed concerns about the use of hydroxychloroquine sulfate for COVID-19 because the drug is used to treat lupus patients and is already in short supply. The FDA has taken steps to redistribute the drug to hospitals for COVID-19 patients despite the lack of extensive clinical trials testing.
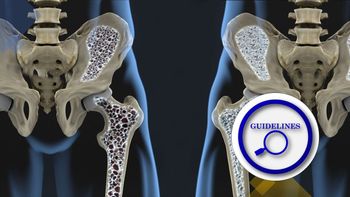
New treatment guidelines for osteoporosis from the Endocrine Society now include romosozumab for postmenopausal women with severe osteoporosis. Learn more in this report.

David Karp, MD, PhD, president-elect of ACR discusses what an appropriate hydroxychloroquine trial would look like, alternate treatment options, and how rheumatology experts should approach their patients during this time.

There is an increasing demand for a therapy that usually faces shortages. ACR provides suggestions for how to approach this and other issues related to hydroxychloroquine and COVID-19.

Gauging joint inflammation via a computer monitor isn't ideal as these are determinations are best done in person, but due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the American College of Rheumatology is encouraging rheumatologists to embrace the technology as physicians increasinly limit the number of in-office visits and as patiets with autoimmune rheumatic disorders increasinly self-isoloate.

Rheumatology patients are more susceptible to infections, making self-quarantining extremely important for this population.

Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus depend on hydroxychloroquine to control disease activity, but demand for this drug, which was already in short supply, has spiked since President Trump championed its use for COVID-19 patients. The American College of Rheumatology has responded by issuing a series of recommendations. Learn more in this article.