Risk factors for cardiovascular disease such as hyperlidipaemia are not being picked up and managed in patients with rheumatology arthritis because it often falls through the gap between rheumatology and primary care provision.

Risk factors for cardiovascular disease such as hyperlidipaemia are not being picked up and managed in patients with rheumatology arthritis because it often falls through the gap between rheumatology and primary care provision.
The risk for osteoarthritis has been linked to a number of genes that are susceptible to epigenetic mediators, shows a new review published in Nature Reviews Rheumatology. The influence of epigenetics on osteoarthritis offers new insights on disease risk.
Outcomes for patients with lupus nephritis, which can lead to irreversible renal impairment, can be improved with better measures to evaluate risk and detect early disease, along with new treatments, say researchers writing in Nature Reviews Rheumatology.
More than 300 million cases of knee and hip osteoarthritis occurred worldwide in 2017.

The recommendations put a strong focus on urate-lowering therapy for gout.

The results must be replicated to prove clinical significance.
In patients with knee osteoarthritis, physical therapy may improve pain and functional disability more so than intraarticular glucocorticoid injections, at one year, according to a head-to-head study published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The rate of serious infections in people with gout, especially sepsis and pneumonia, is increasing, and certain patient characteristics and external factors are associated with both higher healthcare use and in-hospital mortality in these patients, according to one of the first U.S. studies to describe the epidemiology of hospitalized serious infections in gout.

Stress from the possibility of infection can wreak havoc on the mental health and physical well-being of rheumatic disease patients. It usually affects patients in two ways: they either become experts at thwarting infectious disease or they succumb to the stress. In this video, Dr. Kim Gorgens offers tips for identifying stress and anxiety in your patients.
Writing in Practical Pain Management, Don L. Goldenberg, M.D., addresses clinical approaches for managing medications during the COVID-19 pandemic in patients with chronic rheumatic autoimmune disease.
In this Q&A with rheumatologist Nigil Haroon, M.D., Ph.D., of the University Health Network and Krembil Research Institute at the University of Toronto, we discuss COVID-19 factors specific to patients with spondyloarthritis.

Dr. Robinson heads the COVID-19 registry for the Global Rheumatology Alliance, a group that is tracking COVID-19 cases in rheumatology patients worldwide. The group recently published the first set of data from registry in the journal Lancet Rheumatology. In this interview, Dr. Robinson discusses the role of the registry.

High platelet levels within the normal range might be an early indicator for increased risk of osteoporosis, study suggests.
Organic nitrates do not have clinically relevant effects on bone mineral density or bone turnover in postmenopausal women, according to a study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research.

In this interview with Rheumatology Network, Dr. Ellen Gravallese, president of the American College of Rheumatology, addresses the use of telemedicine in rheumatology and how the practice could evolve over time. It may serve to fill gaps in care, she said.
The jury is still out on whether there is a link between the use of bisphosphonates and an increased risk of atrial fibrillation, but doctors prescribing the drugs should bear in mind there may be a link, says the authors of a recent review published online in the Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences.

Patients with severe and progressive rheumatoid arthritis are at risk for joint damage and deformities, especially of the hands, including ulnar deviation and swan neck deformities. In this quiz, we ask five questions on recognizing and treating aggressive rheumatoid arthritis.

There are currently 14 antiviral medications being tested as possible treatments for COVID-19.

Older adults at high risk for knee osteoarthritis can safely engage in physical activities to improve their general health.

Seeing a rheumatologist within 6 weeks did not reduce the severity of radiographic progression.
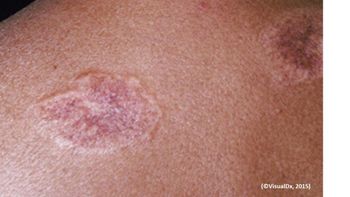
A 38-year-old African American woman visited her doctor complaining of a cough, wheezing, and swollen glands. Can you diagnose this patient?

Mortality rates do not increase for inflammatory bowel disease patients who are exposed to JAK inhibitors.

Zoledronic acid should not be used to treat knee osteoarthritis.

Tele-rheumatology has never really been a predominate feature in rheumatology clinics, but due to the coronavirus pandemic, rheumatology clinics have begun to embrace the practice. Learn more in this interview with Dr. Andrew Concoff, Executive Vice President and Chief Value Officer of United Rheumatology.

Some rheumatology patients have very strong opinions about whether they should continue to take immunosuppressive drugs under the threat of coronavirus. In this interview with Rheumatology Network, Dr. Andrew Concoff, Executive Vice President and Chief Value Officer of United Rheumatology, addresses the hazards of suddenly stopping these medications.

In this interview with Rheumatology Network, Dr. Andrew Concoff, Executive Vice President and Chief Value Officer of United Rheumatology, addresses best practices rheumatology practices may want to consider for managing patient visits.

In this interview with Rheumatology Network, Dr. Andrew Concoff, Executive Vice President and Chief Value Officer of United Rheumatology, discusses how the typical rheumatology patient visit has changed during the coronavirus pandemic.

Patients who have operations have increased range of motion than those who do not have surgery.

Abatacept (Orencia, Bristol Myers Squibb), a T-cell co-stimulation modulator for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile idiopathic arthritis, appears to lower the risk of diabetes mellitus in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who are receiving biologic or targeted synthetic DMARDs.
This week, the National Institutes of Health issued treatment guidelines for the management of COVID-19. It does not include the use of pharmaceutical agents for pre or post-exposure prophylaxis, including hydroxychloroquine, except for within the confines of a clinical trial. This comes as good news to the rheumatology community. More in this article.