
The recommendations put a strong focus on urate-lowering therapy for gout.

The recommendations put a strong focus on urate-lowering therapy for gout.
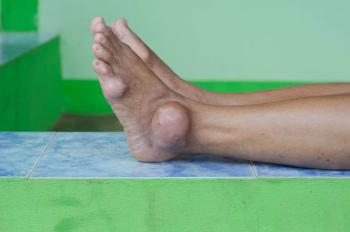
The rate of serious infections in people with gout, especially sepsis and pneumonia, is increasing, and certain patient characteristics and external factors are associated with both higher healthcare use and in-hospital mortality in these patients, according to one of the first U.S. studies to describe the epidemiology of hospitalized serious infections in gout.

Dapansutrile has substantial potential for further development for the treatment of gout flares and other NLRP3-mediated diseases.
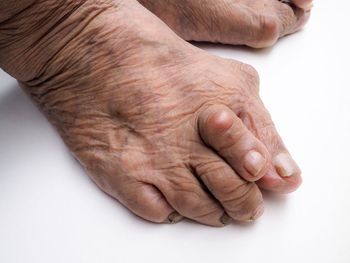
Colchicine, a first-line treatment option for acute gout, is associated with an increased risk of adverse events, such as diarrhea and other gastrointestinal symptoms, but not serious adverse events, finds a newly published systematic review and meta-analysis.
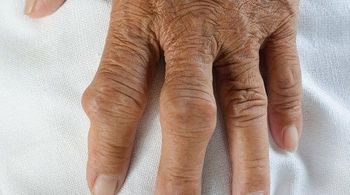
A new study published in the February 5 issue of Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases finds that allopurinol and febuxostat are associated with about the same risk of hypersensitivity reactions, as compared to gout patients treated with colchicine. The risk is even higher for women and diabetes patients, the authors wrote.

Regardless of BMI level, having a genetic susceptibility for gout may be a stronger predictor of disease than weight, say researchers writing in Arthritis and Rheumatology this week.

Compared with other antihypertensive medications, amlodipine was found to reduce risk of gout in older patients.
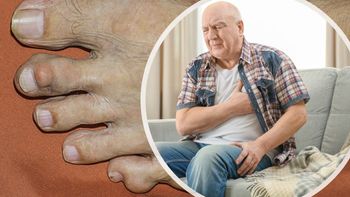
Monosodium urate (MSU) deposits detected by dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) are common in patients with gout and are associated with higher coronary calcium scores, researchers recently reported in JAMA Cardiology.

The suggestion that DECT scans might add to our diagnostic ability to detect cardiac disease may be imprudent because we have tests at our disposal and have little need to increase diagnostic costs. Good clinical judgement, paying attention to traditional risk factors and to red flags, will increase the number of asymptomatic cardiac patients we choose to study with conventional methods.

Abdul Abdellatif, MD, discusses during Kidney Week some treatment options for patients with gout.

Brian LaMoreaux, MD, medical director with Horizon Therapeutics, discusses response to concurrent methotrexate and pegloticase use for treating uncontrolled gout.

ACR Annual Meeting: Gout patients who are admitted to the hospital with worsening heart failure, go on to have gout attacks during hospitalization leading to longer hospital stays, researchers reported November 10 at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology in Atlanta.

American College of Rheumatology officials are offering clinicians an early look at some of the recommendations in the drafted gout guidelines the ACR is set to debut in 2020.

Failure to achieve a target serum urate level of below 6 mg/dL among patients with gout is an independent predictor of total and cardiovascular-related mortality, say researchers writing in RMD Open: Rheumatic & Musculoskeletal Diseases this month.
In a study presented at the Clinical Congress of Rheumatology West held in San Diego last month, researchers led by Brian LaMoreaux, M.D., report that gout was found to be a “a common comorbidity in renal transplant patients.”
Investigators at CCR West find that kidney transplant patients commonly suffer from gout, even before the transplant.

In this week's rheumatology news roundup, we feature a Q&A with Dr. Aryeh M. Abeles who talks with Rheumatology Network about his concerns with the black box warning label for the gout treatment febuxostat. We also include a story on addressing prescription abdandonment in rheumatoloyg. These and other stories in today's news roundup.

Aryeh M. Abeles, M.D., talks with Rheumatology Network about the FDA's black box label for febuxostat, a gout treatment which, according to the results of one clinical trial, was shown to be associated with an increased risk of mortality. In this Q&A, Dr. Abeles, says the decision was based on flawed data.
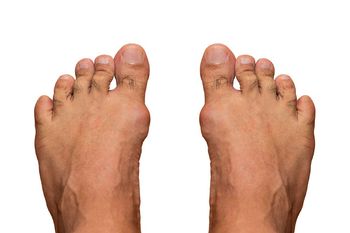
Patients diagnosed with gout at age 40 or younger may be at increased risk for cardiovascular disease and recurrent gout compared to those diagnosed later in life, according to a new study published in ACR Open Rheumatology.
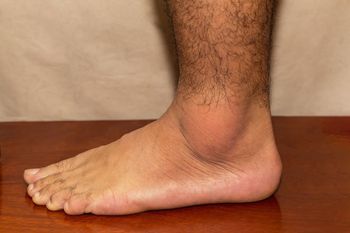
Researchers writing in Arthritis & Rheumatology have found evidence suggesting that osteoarthritis may be a precursor to the development of gout.

While gout does not increase the risk of death post-acute coronary syndrome, a new study suggests it may increase an individual’s risk for readmission after heart failure, as well as the number of days he or she will spend on the hospital.
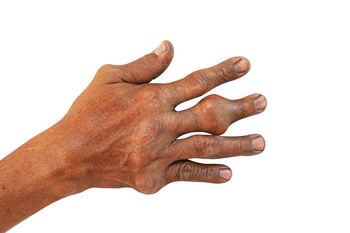
While gout does not increase the risk of death post-acute coronary syndrome, a new study shows the condition does increase an individual’s risk for readmission after heart failure, as well as the number of days he or she will spend on the hospital.

An intensive treatment strategy that combines ebuxostat (Uloric, Takeda) and the novel verinurad, significantly reduced hyperuricemia and albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes patients.

EULAR 2019 wraps this weekend in Madrid. In this slideshow, we highlight some of the most noteworthy findings, beginning with a possible new treatment combination for patients who have both gout and kidney disease.

Despite being the most common form of inflammatory arthritis, gout continues to be poorly managed, new research indicates.