Answer these 8 questions to test your knowledge of the latest research findings.

Answer these 8 questions to test your knowledge of the latest research findings.

This brief slideshow highlights the latest research on gout and its comorbidities.
British researchers build a strong case for closer monitoring of renal function in patients with gout.

Two recent studies examine early characteristics and urate-associated mortality in gout.

Reducing or eliminating these foods may help control gout and minimize frequency of attacks.

Be alert for the development of uveitis in older patients with gout, especially those who have multiple comorbidities.

Patients with obstructive sleep apnea are at increased risk for gout, even beyond the first year after the sleep disorder is diagnosed.

Findings from one of the few studies that have looked at the risk of arrhythmias related to gout in elderly patients.

NSAIDs are currently recommended as first-line therapy but pose the risk of serious adverse effects.
Identifying populations at risk may provide opportunities for primary prevention.

The gout-dementia connection, daily medication reminders, and the impact of interleukin-1β inhibition on gout attacks.

Researchers suggested that anti-oxidants such as Vitamin C and E could delay or even reduce the risk of AMD in patients with gout, as they have been proven to have a beneficial effect in patients with AMD.
Hyperuricemia remains the leading risk factor, but the runners-up may surprise you.

Here: the latest evidence on the effects of febuxostat, allopurinol, and statins on CV mortality in patients with gout.
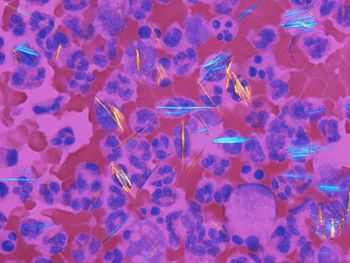
The time to revisit treatment approaches for gout is now.

Despite its antioxidant properties, uric acid may not be as neuroprotective as previously thought.

Recent findings call into question the safety of long-term febuxostat therapy in patients with cardiovascular disease.
Should urate-lowering therapy be continued during an acute gout attack? Which antihypertensive has mild uricosuric effects? Test yourself with these questions and more.

Among the highlights of 3 recent studies: insights into hormonal risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis.
A green light for dosing to achieve the target urate level.

The latest recommendations emphasize providing key information about the disease and its treatment.

A quick summary of the 2012 American College of Rheumatology guidelines for the management of gout.
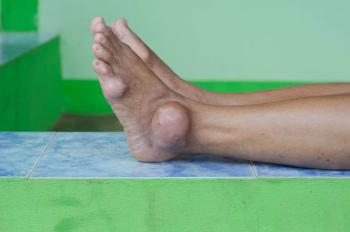
For gout patients with suboptimal responses to allopurinol, adding lesinurad may significantly reduce serum urate levels.
Researchers rank febuxostat as the most effective urate-lowering drug for reaching serum uric acid targets for gout patients.

Gout’s relationship with food intake can be tricky, so which is better: Eating foods lower on the glycemic index scale or lower in carbohydrates?