
Depression may be linked to an increased risk of rheumatoid arthritis, particularly patients taking antidepressants, shows a new study.

Depression may be linked to an increased risk of rheumatoid arthritis, particularly patients taking antidepressants, shows a new study.

Weight fluctuation in rheumatoid arthritis patients appears to be associated with higher cardiovascular risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, especially if they are not overweight, shows a new study.

Just 2% of observed older men to experience an indicative fracture received a diagnosis and treatment for osteoporosis over a four-year period.

An analysis of data from more than 65k patients suggests low-dose CT scans could provide an opportunity to screen for osteoporosis in older patients.

New survey findings show the antimalarial drug's promotion for potential SARS-CoV-2 benefit early into the pandemic led to needing patients losing access.

Data suggest patients administered tofacitinib for their arthritis do not face worsened risk, severity of flu infection.

The first 3 months of the pandemic were marked by a significant rate of patients changing or discontinuing medication without clinician guidance.

New data show patients with arthritis and psoriasis are far more likely to quarantine and isolate than similar patients, differentiating by treatment type.

New data from ACR 2020 assure concerns that patients with arthritis who test positive for COVID-19 may be at worse risk of ICU admission or even death.

Risk of herpes zoster and creatine phosphokinase increased with use of upadacitinib.
Anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive agents are the two primary classes of drugs used to treat lupus nephritis. Now, a new study shows that the addition of the monoclonal antibody belimumab to standard therapy may make a meaningful difference in this hard-to-treat patient population.
Although mortality rates for kidney transplant recipients with COVID-19 are known to be high, end stage kidney disease patients with COVID-19 appear to have a higher risk of mortality than patients with new kidneys.

A possible new treatment for advanced lupus nephritis passes a phase two trial, according to a study presented at Kidney Week, the annual meeting of the American Society for Nephrology. The treatment, a CD20 antagonist called obinutuzumab, led to improvements in 41 percent of patients with lupus nephritis—a condition that affects one in 60 people with systemic lupus.
An analysis of data from 12k women in an ongoing Finnish study suggests obesity could signal increased risk for early hip fracture in postmenopausal women.

Results of a study from ASN Kidney Week 2020 suggests low bone mineral density rates among women with CKD varied according to kidney function and race/ethnicity.
The gout treatment allopurinol doesn't appear to slow the progression of chronic kidney disease in patients with moderate to severe loss of kidney function, shows a study presented yesterday at the American Society of Nephrology Kidney Week annual meeting.
Treatments for lupus nephritis can cost patients over $50,000 a year, according to a study presented yesterday at the American Society of Nephrology Kidney Week annual meeting.

An analysis of more than 240 postmenopausal women with osteoporosis offers a glimpse into potential predictors of osteosarcopenia in this patient population.

A recent analysis suggests increased exposure to inhaled or oral corticosteroids was linked to an increased risk of osteoporosis and fragility fractures.

Children who take oral corticosteroids for autoimmune conditions, such as juvenile arthritis, psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease or other conditions, like asthma, have an increased risk of diabetes, high blood pressure, and blood clots, say researchers writing in the American Journal of Epidemiology.
A new study published in the Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons shows that patients with advanced osteoarthritis who undergo total joint replacement, significantly lower their risk of falls after surgery as compared to patients who opt out of surgery.

An analysis of more than 140 patients from a hospital in Italy suggests spinal fractures could help predict which patients were at an increased risk for negative outcomes with COVID-19.

An analysis of GoogleAnalytics data suggests use of FRAX fracture risk assessments declined by 58% globally in April 2020 compared to February 2020.
A study published in the New England Journal of Medicine earlier this year of patients with sciatica lasting longer than four months due to lumbar disk herniation, finds that microdiskectomy was superior to nonsurgical care in controlling pain six months post-op.
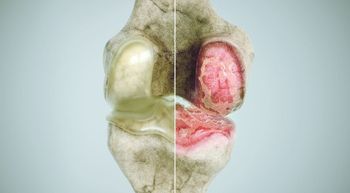
Researchers have created a machine-learning algorithm that can detect subtle signs of osteoarthritis—too abstract to register in the eye of a trained radiologist—on an MRI scan taken years before symptoms even begin.

An analysis of 22k prostate cancer patients over a 15-year period suggests less than 1-in-4 undergo bone mineral density testing after androgen deprivation therapy.

A year from now, with all the luck and scientific progress in the world, we’ll be free to roam again. There may be a whole raft of new stressors waiting for us, but the work you do now to help keep your patients mentally healthy will pay off in meaningful ways.

Numbers of a new type of cell discovered in the blood of rheumatoid arthritis patients increase dramatically immediately before a flare.

The underlying pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis with and without autoantibodies may be different. Researchers say that "it is time to formally subdivide RA into type 1 (with autoantibodies) and type 2 (without autoantibodies)."
In this week's news roundup from Rheumatology Network, we highlight this week's leading stories including two stories on new developments in osteoporosis treatment. In one, a physician-scientist describes "a crisis in the treatment of osteoporosis" due to severe side effects. Learn more about this story and others in this week's news roundup.