
Patients who cannot tolerate cDMARDs may experience additional value from tocilizumab compared to adalimumab.

Patients who cannot tolerate cDMARDs may experience additional value from tocilizumab compared to adalimumab.

Rheumatoid arthritis patients with probably major depressive disorder or generalized anxiety disorder were more likely to suffer from worse fatigue and pain.

A team investigated data from trials of tofacitinib, adalimumab, and placebo.

The safety profile of upadacitinib is consistent with phase 3 rheumatoid arthritis studies.

The incidence rate of serious infection events and opportunistic infections was higher among the upadacitinib 30 mg group than the 15 mg group.

In a late-breaking abstract, investigators test nanoparticle treatment using in vivo models.

The findings are important to understand treatment persistence and switch patterns in rheumatoid arthritis patients with poor prognostic factors in a real-world setting.

The results highlight a significant improvement in rheumatoid arthritis signs and symptoms for those who used upadacitinib over placebo and adalimumab.

In a study presented at EULAR, investigators find 14-3-3η baseline levels did not correlate with baseline mTSS.

Patients are unaffected by the switch from ADL-EU to ADL-PF.
Researchers writing in Arthritis and Rheumatology report that high levels of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (anti-CCP2) appear to be markers for future cardiovascular events in rheumatoid arthritis patients.

Glucocorticoids are the most frequently used class of drugs for rheumatoid arthritis because they are effective at relieving symptoms, and widely available at low cost. While this drug class has clear benefits for rheumatoid arthritis, it comes at a price in terms of a wide array of potential side-effects. Test your knowledge on the use of corticosteroids in rheumatoid arthritis with this quiz.
Rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes may be closely related, according to researchers writing in the June issue of Arthritis and Rheumatology.







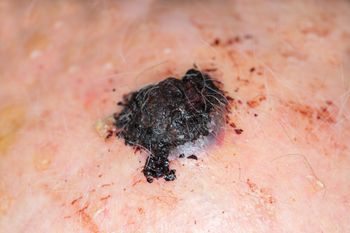
Researchers writing in JAMA Dermatology this week report that patients with inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriasis who are treated with biologics may have a "clinically meaningful" increase in melanoma risk, but the jury is still out.
There is no significant association between biologic exposure and the development of melanoma in patients with IBD, rheumatoid arthritis, or psoriasis.
Data collected by doctors in Italy when the country was hit by COVID-19 should allow rheumatologists to feel more comfortable in advising patients with chronic arthritis to continue taking immunosuppressive targeted therapies. The data show that chronic arthritis patients treated with DMARDs do not seem to be at increased risk of respiratory or life-threatening complications from SARS-CoV-2.
Risk factors for cardiovascular disease such as hyperlidipaemia are not being picked up and managed in patients with rheumatology arthritis because it often falls through the gap between rheumatology and primary care provision.

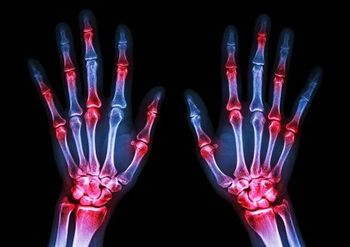
Patients with severe and progressive rheumatoid arthritis are at risk for joint damage and deformities, especially of the hands, including ulnar deviation and swan neck deformities. In this quiz, we ask five questions on recognizing and treating aggressive rheumatoid arthritis.