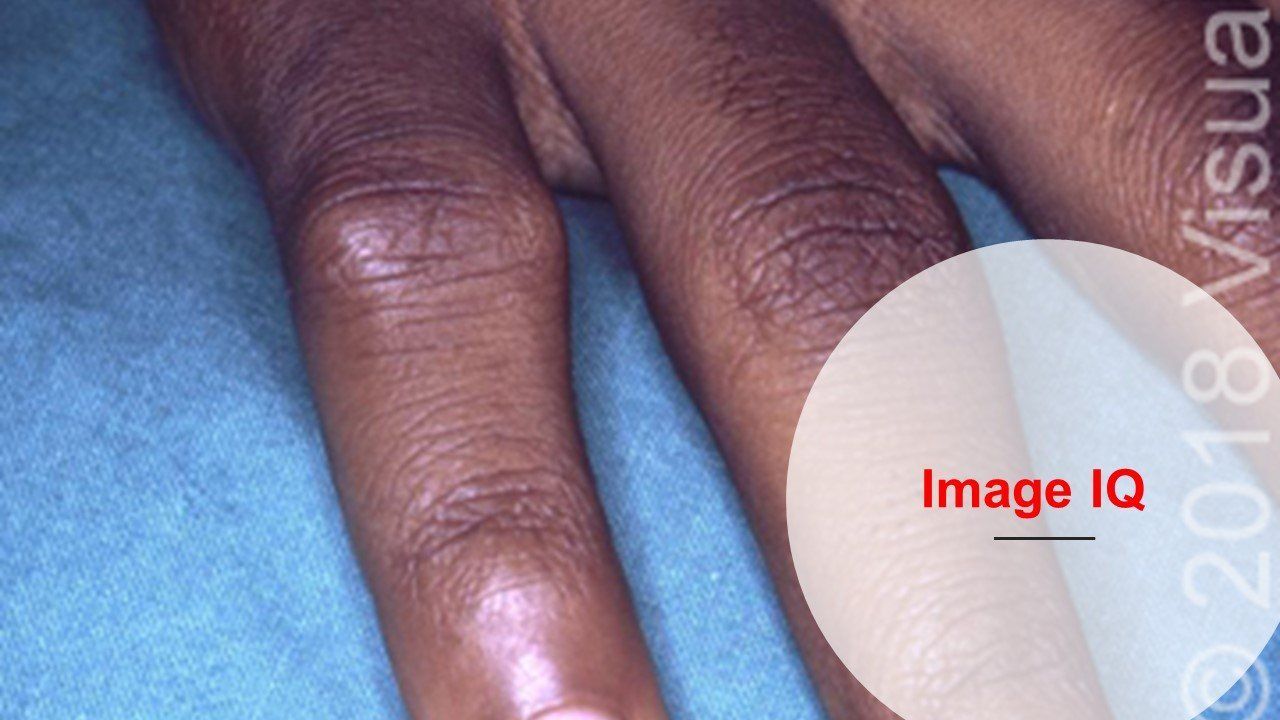
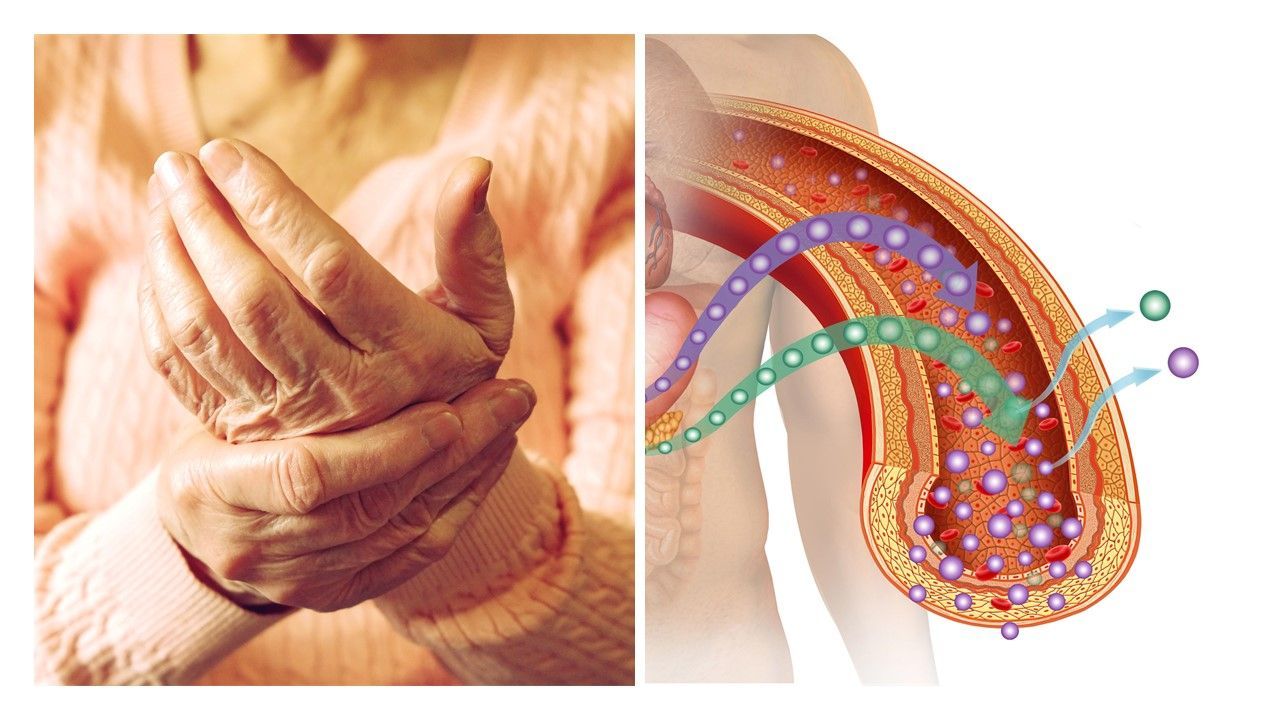
Studies that explore the efficacy and safety of JAK inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis are among those we selected as most noteworthy in 2019. Also, at the top of the list, a study that shows glucocorticoids, not necessarily biologics, raise the infection risk after joint replacement surgery. Learn more in this slideshow.