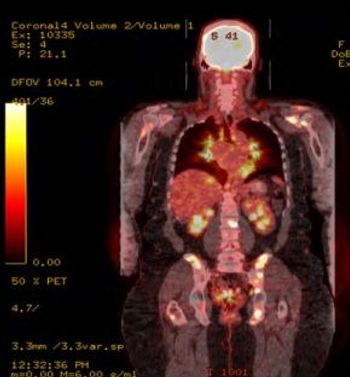
A 56-year-old woman presents with a history of intermittent shoulder pain for the past six months. Early signs point to bursitis, but the plot thickens: She also has sarcoidosis and lymphoma. How would you proceed?

A 56-year-old woman presents with a history of intermittent shoulder pain for the past six months. Early signs point to bursitis, but the plot thickens: She also has sarcoidosis and lymphoma. How would you proceed?

In lupus patients, urinary CD4 T cell counts correlate selectively and specifically with disease activity and renal involvement, well enough to be used to monitor the progress of treatment.
One orthopedic surgeon estimates University of Louisville sophomore guard Kevin Ware will return to the basketball court after six months of healing and rehabilitation following emergency surgery on the athlete's compound fracture in his right tibia.

Iron-deficiency anemia appears to be a good indicator of rapid progression of erosive rheumatoid arthritis not seen using standard disease activity measures.

(AUDIO) Intensive analysis of protein pathways inside joints is showing strong activity among messengers involved in wound healing. In this podcast, learn about the new research that backs the vision of arthritis as a chronic wound, and the implications for management.

New in the New England Journal this week: Skeletal fluorosis from consumption of very strong tea, and a lack of proven benefit for arthroscopic partial meniscectomy.
New research suggests that obesity is not merely a physical force on the knee joint; adipose cells contribute biochemically to inflammation and pain. What are the implications for management of obese patients who need knee replacement surgery?

The largest randomized controlled trial (RCT) so far has found no benefit to arthroscopic partial meniscectomy (APM) even in patients with symptomatic meniscal tears. An editorial advises against the procedure except when physical therapy has not helped at all.

The great majority of knee replacements last for at least 20 years in juvenile arthritis patients, a multicenter study finds. Hip replacements are more problematic.

As more than 60 percent of women with temporomandibular disorders (TMD) also exhibit abdominal pain consistent with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms, two researchers in the neural and pain sciences department of the University of Maryland School of Dentistry, in Baltimore, have developed a model to better illustrate the two conditions' comorbidity.

The RADAI joint index designed for rheumatoid arthritis patients provides equally powerful information about disease status in osteoarthritis and psoriatic arthritis, according to a new comparative study. As a guide to severity, it is much quicker than waiting for lab results to come in.
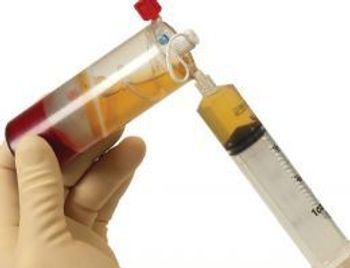
Sports medicine clinicians from the Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS), in New York City, report that platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections improve joint pain and function in patients with osteoarthritis, a leading cause of disability that affects more than 47 million people in the United States.

Here's a notice for your waiting room bulletin board: Manufacturers are recalling Reumofan Plus, an herbal supplement marketed as "100% natural," found to contain active pharmaceutical ingredients not listed on the packaging.

Beyond the discovery of new disease genes, revelations about how how our microbes influence our immunity and about many new subtypes of T cells--a mixture of commitment and plascticity.

Evidence-based analysis shows that weak opioids have at best a weak effect in rheumatoid arthritis pain. Steroid injections offer no long-term relief for tennis elbow.
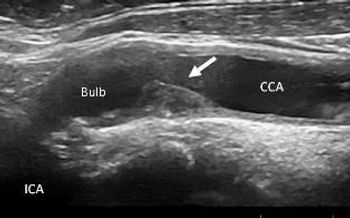
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis are at considerably increased risk of asymptomatic carotid artery disease, but standard scores have proven poor predictors of their actual cardiovascular risk. Special vigilance is warranted for these patients.

Does this evidence from recent research overturn some generally accepted principles about gout, rheumatoid arthritis, reactive arthritis, and osteoarthritis? Most of these studies were undertaken in order to test ideas that were described as common wisdom in rheumatology.

Rare systemic adverse reactions to corticosteroid injections for juvenile idiopathic arthritis are described in a review of an institution's cases and the literature.

Test your skills about the diagnosis and treatment of osteoporosis in this brief quiz offered by Nancy Lane MD.

A small sham-controlled trial has shown significant differences in pain processing among fibromyalgia patients who used an FDA-approved device for at-home cranial electrical stimulation. It is evidently the first study to use fMRI to test the concept.

Research published within the past year has increased and refined support for the concept that this autoimmunity may arise initially in mucosal surfaces, predominantly the lung, the oral cavity, and the digestive system, prompted by the presence of microbes.

Reviews describe the JAK/STAT pathway that has proven successful against rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory conditions, and the many other pathways that govern inflammation, often to the detriment of anti-inflammatory strategies.

Used for gout for centuries, colchicine is known to be peculiarly toxic at high doses. A new understanding of its potential for poisoning, deliberate or otherwise, merits attention to its often-underestimated risks.

A closer look at racial disparities in treatments for rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis show nuanced explanations for why African Americans are less willing to undergo drug therapy and surgery. More careful and clearer communication may go a long way toward closing the gap.

Does the research show any significant difference between anti-tumor necrosis factor drugs in terms of their effectiveness for treating psoriatic arthritis?

With most medical schools devoting only a few curriculum hours to pain management training, many physicians begin their medical career underprepared to meet the needs of patients suffering with chronic pain. Here, Barry Cole, MD, identifies several key concepts that would help improve pain care in the US if only more physicians would learn about them sooner.

Recently, a group calling itself Physicians for the Responsible Opioid Prescribing proposed several radical changes to the way we treat patients with chronic noncancer pain, calling for limits on the dose and duration of opioid treatment that would in effect deny these medications to the majority of patients now receiving them for noncancer pain.

The variety of mechanisms that play a part in pathologic pain perception leads to a great deal of complexity and variation in the clinical presentation and severity of fibromyalgia symptoms, as well as a high degree of variability in patient response to treatment.

Refining the ample evidence that rheumatologists and their rheumatoid arthritis patients disagree on the severity of symptoms, new studies reported at ACR2012 point toward better definitions of disease status, and a way to identify patients for whom treatment targets may need to be reconsidered.

Results presented at the American College of Rheumatology/Association of Rheumatology Professionals 2012 annual meeting show that adalimumab and methotrexate are more effective than DMARDs and prednisone in achieving remission in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis or undifferentiated arthritis patients.