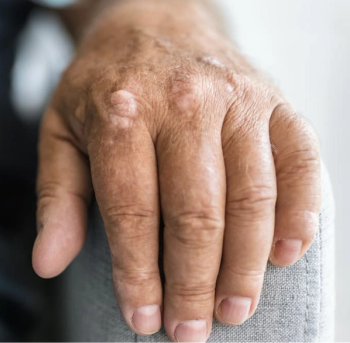
Psoriatic Arthritis
Latest News
Latest Videos

Podcasts
More News

Explore five pivotal FDA decisions set for early 2026 that could transform specialty medicine and enhance treatment options across various conditions.

This rheumatology month in review emphasizes new data from the ACR Convergence.

In long-term follow-up of KEEPsAKE 1 and 2, risankizumab maintained joint, skin, pain, and axial responses in patients with PsA through 244 weeks.

Sonelokimab meets ACR50 primary endpoint in a phase 2 trial.

Stay updated with the latest healthcare breakthroughs, including FDA news, regulatory submissions, and evolocumab data for ASCVD, in this week's essential news roundup.

The approval makes guselkumab the first and only IL-23 inhibitor approved for these pediatric indications and was based on data from the phase 3 PROTOSTAR study.

Risankizumab shows significant and lasting improvements in psoriatic arthritis symptoms, addressing multiple disease domains and enhancing patient quality of life.
A new meta-analysis has contrasted the association between the 2 conditions against the general population, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis.

Combining golimumab with methotrexate reduced corticosteroid reliance and maintained efficacy in psoriatic arthritis.

In this feature, 3 experts discuss the management of 2 overlapping conditions: psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.

DRESS-PS extension study shows patients maintaining low disease activity while gradually reducing TNF inhibitor doses over 24 months.

The APEX study presents the results of 2 dosing regimens of guselkumab (Q4W and Q8W) in biologic-naïve patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA).

Guselkumab shows promise as the first IL-23 inhibitor to significantly reduce joint damage in active psoriatic arthritis.
New phase 3 trials reveal tildrakizumab 100mg significantly improves symptoms in active psoriatic arthritis, offering hope for effective treatment options.

Conversely, influenza vaccine was associated with increased COVID-19 severity and hospitalizations in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases.

Bristol Myers Squibb's deucravacitinib shows promise as a safe, effective treatment for active psoriatic arthritis, pending FDA approval by March 2026.
Findings suggest clinical risk factors involved in the development of psoriatic arthritis in children with psoriasis, including BMI and psoriasis location.

TYK2 inhibition may offer a potentially better tolerated treatment option than JAK inhibitors for people with PsA.

Mease outlined positive efficacy and safety findings from multiple long-term follow-up trials of the biologic in people with PsA and AxSpA.

Presented at SDPA, the FOREMOST Trial showed apremilast reduces joint burden and improves function in early oligo PsA through week 48.

Depressive symptoms in the first 2 years after diagnosis were linked to lower odds of achieving remission in both RA and PsA.

New Phase 3 trial results reveal deucravacitinib's effectiveness in treating active psoriatic arthritis, offering hope for improved patient outcomes.

New research highlights deucravacitinib's effectiveness in alleviating both skin and joint symptoms in people with both psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.

Patients with concurrent type 2 diabetes mellitus and psoriatic arthritis who have a BMI below 30 kg/m2 exhibit higher all-cause mortality and lower 5-year survivability than those with higher BMI measurements.