
Gout is on the rise globally. A Brazilian researcher who surveyed that nation's rheumatologists found some are ignoring--or unaware of--guidelines on how to treat the ailment.

Gout is on the rise globally. A Brazilian researcher who surveyed that nation's rheumatologists found some are ignoring--or unaware of--guidelines on how to treat the ailment.
Ankylosing spondylitis appears to carry an increased risk of vascular mortality, Canadian researchers report.

While Lyme disease cases tend to peak during the summer months, the threat is not over once the weather cools down. But as recently discovered, a single test may not be enough for an accurate diagnosis.
A study of patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty found that patients with psoriatic arthritis face no greater risk of poor outcomes than patients who get hip replacements because of osteoarthritis.
A study in BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders suggests that multinucleated giant cells (MGC) may contribute to osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in addition to their known association with synovitis severity. The finding adds to other recent research and points to the therapeutic potential of targeting MGCs to improve pain and joint damage in both types of arthritis.
A study in PLOS One found evidence that fat metaplasia in sacroiliac joints (SIJ) is significantly associated with spinal progression for axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA).
Gout has been making quite a stir in news recently. Between a new classification system and a study showing that a common food can cause painful flares, this form of arthritis is getting quite a bit of attention. Now comes word that a drug used to treat gout could also be effective for another damaging condition.
Study shows that patients with psoriatic arthritis and cutaneous psoriasis could be good candidates for total hip replacement.
Research shows a possible biological basis between gout, tomatoes and other foods.

Regulators in the UK have decided not to recommend apremilast as an alternative to DMARD therapy in patients with psoriatic arthritis.

Evidence-based medicine and patient input needed in prescribing bisphosphonates for osteoporosis.

Researchers have found further links between vitamin D deficiency and chronic inflammatory rheumatic diseases such as psoriatic arthritis.
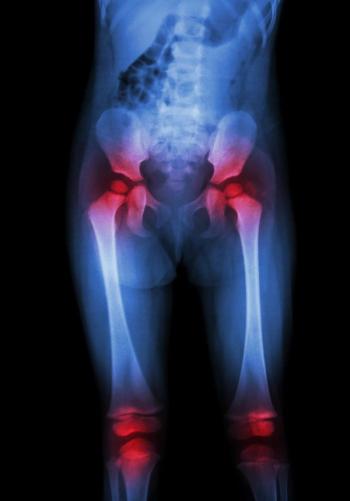
Distinguishing between different types of childhood arthritis is not always easy.
The first study of its kind examined joint replacement surgery in patients with osteoarthritis and confirmed an increased risk of cardiovascular complications.

A study in JAMA Dermatology provides evidence that the use of two tests to assess cutaneous sarcoidosis disease severity should be expanded. The research has applications for dermatologists, rheumatologists, and pulmonologists, all of whom have a role in treating sarcoidosis.

A new study in Nutrition Journal shows that patients suffering from systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) demonstrated significant improvement by taking fish oil supplements.

In rheumatoid arthritis there is an ongoing debate about what to do when methotrexate fails. Physicians typically have two choices.

Biologics can improve the quality of life for RA patients, but side effects remain a problem, especially for RA patients with co-morbidities.

A systematic review of alopecia areata (AA) in Clinical, Cosmetic & Investigational Dermatology highlighted the unpredictability and lack of treatment options for the condition. But it also pointed to a larger problem: more than half of patients with AA experience poor health-related quality of life (QOL). Patients with AA are at risk for depression and anxiety, atopy, vitiligo, thyroid disease, and other autoimmune conditions.

Patients with fibromyalgia typically experience widespread chronic pain and a new study adds to the evidence that emotional impact is prominent as well.

A recent study in The Journal of Headache and Pain sheds some additional light on the chronobiological experience of patients with cluster headache (CH). However, it still leaves lingering mysteries around the pattern of pain CH that patients typically experience, the triggers of those headaches, and the mechanisms and interactions that drive headache frequency and severity.
Researchers found that adding kunzea oil to topical psoriasis treatments with liquor carbonis detergens (LCD) and salicylic acid did not improve the irritating skin condition.

B-cells that are active in lupus may also play a role in Sjögren’s syndrome. A new study finds that the same B-cell depleter drug, belimumab (Benlysta) approved for lupus, may also benefit Sjögren’s patients.

Social stressors, such as being treated poorly in a doctor’s office, can lead to negative disease outcomes, particularly among black women with lupus, a new study shows.
In one of the first large-scale studies designed to assess the risk of vascular mortality in patients with ankylosing spondylitis, researchers have found that patients with ankylosing spondylitis have a significantly higher risk for vascular death as compared to healthy populations.

A small Italian study found no evidence that use of anti-TNF-alpha agents during pregnancy affects the health or development of children in their first 2 years of life.
Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is one of the pain conditions that has remained fairly mysterious, but a new, effective treatment may be on the horizon. It is known that CRPS most often develops following trauma, however, and evidence suggests a maladaptive response to nervous system damage involving immune and inflammatory pathways as well as abnormalities in both peripheral and central processing of afferent inputs. No single therapy – including pharmacologic therapy – wholly addresses the condition.
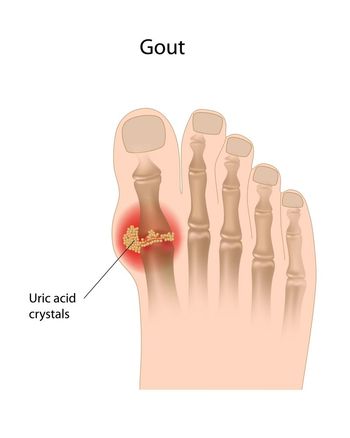
Patients with tophaceous gout rarely develop ulcers, but when they do occur, these ulcers can be difficult to treat. This case study explores the diagnosis of and treatment options for patients with ulcerated tophaceous gout.


Up to one-third of people with active ankylosing spondylitis (AS) have some degree of bone loss due to systemic inflammation and decreased mobility, but lowering inflammation with tumor necrosis factor blockers may improve bone density.