
A case-controlled study of 60 patients in the United Kingdom found presence neuropathy contributes to fracture risk in patients with type 1 diabetes but found other factors play a role in the increased risk among these patients.

A case-controlled study of 60 patients in the United Kingdom found presence neuropathy contributes to fracture risk in patients with type 1 diabetes but found other factors play a role in the increased risk among these patients.

Take 5 minutes to catch up on Rheumatology Network's highlights from the week ending April 2, 2021.

COVID-19 has created new challenges and opportunities in the way that rheumatologists care for chronically ill patients, including the introduction and prevalence of telemedicine and digital health applications (DHAs).

Mortality rates were similar in COVID-19 patients with and without chronic inflammatory diseases.

While some patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) find it beneficial to receive anti-inflammatory therapy to treat their fatigue, there is increasingly more evidence that chronic diseases increase risk of psychiatric disorders, such as anxiety and depression, which need to be treated differently.

Recently, a link between venous thromboembolism (VTE) and Janus Kinase (JAK) inhibitors has emerged, causing the FDA to recommend a black box label for tofacitinib in 2019. New research, however, suggests that tofacitinib had similarly infrequent cases of VTE (<1 per 100) when compared with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFIs).
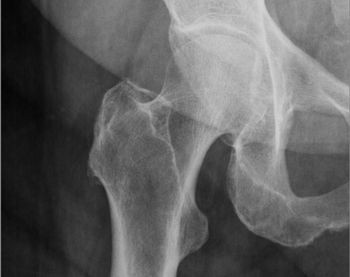
Despite lower length of stays, costs of hip fracture surgeries have been on the rise in recent years and a new study suggests it could be linked to increased hospital charges rather than increased surgeon charges.

Investigators identified both facilitators and barriers for trial participation in patients at risk for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in order to enhance inclusion in trials designed to prevent RA.

The difficult-to-treat disease has a multitude of symptoms to address with a wide spectrum of agents.
A meta-analysis notes that relative risk for stroke was high for rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, and gout.

This week, Rheumatology Network interviewed Michael C. Schweitz, MD, to discuss the recent press release published by CreakyJoints that announced their partnership with the John Whelton Arthur Virshup CreakyJoints South Florida Arthritis Clinic.

Patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases (IRD) may be more likely to acquire severe pneumonia due to COVID-19, especially in patients with autoimmune disease who are being treated with rituximab.

Currently, diagnosing a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a complex process that compares potential lupus with other conditions. It can be challenging and delayed by a period of time, which increases patient uncertainty, referrals, healthcare utilization, increased flares, and organ dysfunction. In this study, machine learning (ML) via artificial intelligence tools based on patient data was used to develop an algorithm to help with SLE diagnosis.

Switching from 60 mg to 30 mg denosumab every 6 months could be an option for patients who have completed long-term denosumab therapy, according to the results of a new study from McMaster University.

Most women experience a decrease in the severity of their rheumatoid arthritis (RA) symptoms during pregnancy, but some may need ongoing treatment. Test your knowledge of the treatment of RA during pregnancy.

During the study, which ran from December 2016 through May 2018, 301 flares were treated: 214 with anakinra and 87 with triamcinolone. Both treatment options reduced pain intensity for both first and subsequent flares.

Take 5 minutes to catch up on Rheumatology Network's highlights from the week ending March 19, 2021.
A Mass General-led analysis of claims data indicates less than 1-in-10 patients who suffer a hip fracture were prescribed an osteoporosis treatment in the next 6 months, while also providing data on trends in prescribing practices of newer agents.

Guselkumab is the first and only approved IL-23 inhibitor therapy used to treat adults with active PsA and moderate to severe plaque psoriasis (PsO). The medication showed efficacy in skin clearance and joint symptom relief and passed safety measures. Additionally, physical function, health-related quality of life, and resolution of enthesitis and dactylitis were confirmed through week 100.

The diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) may be delayed by more than 2 years in half of patients, especially those of younger age at symptom onset, or with a higher body mass index (BMI) or enthesitis before diagnosis.

A majority of patients with active psoriatic arthritis achieved and maintained skin clearance, joint symptom relief through year 2 of treatment.
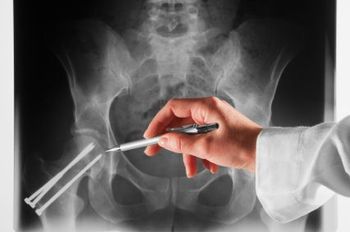
Using data from the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men study, new research suggests incorporating AAC scores and PVFx could help predict older men at increased risk of fractures.

Although associated with adverse effects, glucocorticoids are effective for managing rheumatoid arthritis (RA) symptoms and are prescribed to most patients. Test your knowledge of the prescription of glucocorticoids in RA with this quiz.

Take 5 minutes to catch up on Rheumatology Network's highlights from the week ending March 12, 2021.

Pegloticase (pegylated uricase) is medication approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) designed to lower sUA in patients with uncontrolled gout. However, 26% of patients have infusion-related reactions (IRs), which may be indicative of the development of antidrug antibodies (ADAs). Due to this, physicians often administer immunomodulators in addition to pegloticase in order to prevent ADAs as well as increase the effectiveness of the therapy.

There were no differences in the occurrence of clinical characteristics between the subset of patients with and without neurological involvement, however disease activity was slightly higher in patients with neurological involvement than those without. Additionally, anti-SSA antibody was significantly higher in patients with neurological involvement and anti-SSB autoantibody was lower.


Older adults who self-report rheumatoid arthritis (RA) do not have a Medicare claims history consistent with their diagnosis, according to study.

Subcutaneous injection of tocilizumab has been shown to improve the rate of lung function in patients with systemic sclerosis-induced interstitial lung disease when compared with a placebo.

Research suggests that adults who experienced 2 or more traumatic events during childhood are at a 100% increased risk to develop rheumatic disease.