
Results revealed 92.45% of patients with fibromyalgia were simultaneously diagnosed with at least 1 type of psychiatric disorder, although most were diagnosed with 2 or more.

Results revealed 92.45% of patients with fibromyalgia were simultaneously diagnosed with at least 1 type of psychiatric disorder, although most were diagnosed with 2 or more.

Results of a recent study found that fibromyalgia may be more common among individuals with opioid use disorder, and that treating fibromyalgia may be beneficial for treating opioid use disorder.

Patients with fibromyalgia were more likely to report that pain caused them to continue using opioids, to increase the amount of opioids they used over time, and to delay getting addiction treatment.

At week 24, serum IGF-1 levels increased and body weight was reduced by an average of 6.5% from baseline.

Although the ultimate results of the study were unsurprising to Shai Efrati, MD, PhD, the magnitude of improvement was much higher than he and his team had anticipated.

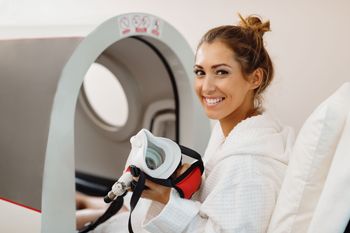
Results of a recent study indicated that hyperbaric oxygen therapy significantly relieved symptoms of fibromyalgia.

Adult patients with traumatic brain injury-induced fibromyalgia were randomized 1:1 to receive hyperbaric oxygen therapy or pharmacological intervention.

New cohort analysis data show women with fibromyalgia are at an increased risk of depression—which is also correlated with a worse life expectancy over 8 years.

Compared with the control group, patients in the exercise for wellbeing (Qi Gong) and physiotherapy groups reported statistically significant improvements at week 5 in joint range of movement, muscle strength, spirometry, and quality of life.

Improvements may be due in part to the association between weight loss and fewer pain symptoms in patients with fibromyalgia.

Results of a recent study indicated that when a patient is able to temper their underlying disease, it can improve their experience of centrally sensitized pain despite not obtaining low disease activity.

Investigators hypothesized that patients with fibromyalgia who avoid activities because of pain would be more likely to perceive more intense pain levels after walking due to catastrophizing.
The majority of included studies observed improvements in pain, fatigue, patient global, sleep disturbance, multidimensional function, and tender points.

An international review of data show certain antidepressants may benefit conditions like fibromyalgia, but many trials are actually inconclusive.

Investigators measured pain intensity, the primary outcome, as well as physical function, isometric strength, quality of life, and fibromyalgia impact at baseline and the 6-month mark.

The January 2023 rheumatology month in review highlights a recent study that indicated an increased risk of hospitalization and death among patients with gout and COVID-19, the expansion of research evaluating adalimumab biosimilars, and trends in fibromyalgia.

Single and dual-task conditions were implemented to determine the reliability of the 3MBWT alongside the Timed Up and Go test in assessing balance-related fibromyalgia symptoms.

New research has helped to validate a predictive design model created to identify those most at risk for developing fibromyalgia.
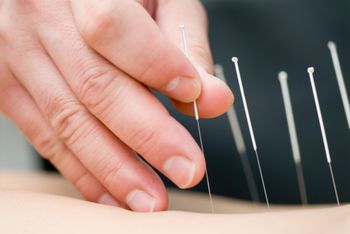
The findings visualized the increased amount of research regarding acupuncture for fibromyalgia treatment, which may eventually boost efficacy, reduce cost, and promte future development in the field.

Improved patient-reported outcomes were observed in patients who used mind-body interventions, such as cognitive behavioral therapy and yoga, and were effective for managing IBS and fibromyalgia.

Intervention strategies that focus on the reduction of catastrophic thinking in addition to physical exercise may be beneficial for patients with fibromyalgia.

The cross-sectional study evaluated the relationship between the mediating variable, distress, and pain and functionality in patients with fibromyalgia after controlling for age, gender, and income.

“Although the evolution of COVID-19 is favorable worldwide, multiple variables related to psychological health and the response to stressors seem to have triggered symptomatologic responses in fibromyalgia patients,” investigators stated.

Although high intensity resistance training did not improve mood in women with fibromyalgia, anger decreased during the 8-week, supervised intervention program.

Current literature is trending towards exploring the impact of complementary and alternative treatments for fibromyalgia and an overall focus on multidisciplinary care.