
With the exception of duloxetine, milnacipran, and pregabalin, most therapies exhibited insignificant results in reducing pain.

With the exception of duloxetine, milnacipran, and pregabalin, most therapies exhibited insignificant results in reducing pain.

New findings suggest Mu-Lympho-Marker could serve as a reliable biomarker for chronic pain in fibromyalgia, enhancing diagnosis and treatment strategies.

Depressive symptoms in the first 2 years after diagnosis were linked to lower odds of achieving remission in both RA and PsA.

Inebilizumab was approved by the FDA under the name Uplizna as the first and only treatment for adult patients with IgG4-RD in April 2025

New findings reveal upadacitinib's effectiveness in treating giant cell arteritis, highlighting reduced infection rates with shorter glucocorticoid tapering.

The findings are the latest from a series of trials seeking to decrease treatment burden for patients with uncontrolled gout.

New Phase 3 trial results reveal deucravacitinib's effectiveness in treating active psoriatic arthritis, offering hope for improved patient outcomes.
Recent studies reveal belimumab's effectiveness in treating lupus nephritis, showing significant renal response and improved patient outcomes in real-world settings.

New research highlights deucravacitinib's effectiveness in alleviating both skin and joint symptoms in people with both psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.

Patients with concurrent type 2 diabetes mellitus and psoriatic arthritis who have a BMI below 30 kg/m2 exhibit higher all-cause mortality and lower 5-year survivability than those with higher BMI measurements.
Early results show efzofitimod's promise in treating systemic sclerosis-related interstitial lung disease, with significant skin improvement in patients.
New analysis reveals obinutuzumab's potential to improve kidney inflammation and biomarkers in lupus nephritis.

The rheumatology month in review emphasizes new research in gout burden, fibromyalgia management, and innovative lupus treatments.

A recent study reveals significant variations in biologic use among pregnant patients with autoimmune diseases, highlighting the need for tailored risk-benefit assessments.

This FDA News Month in Review provides a round-up of regulatory decisions from May 2025.

However, a significant effect was seen in a subgroup of participants with severe pain (VAS score ≥ 80 mm) at baseline.

A new study reveals immersive virtual reality exercise reduces perceived pain in fibromyalgia patients, highlighting its potential for chronic pain management.
Epaminurad effectively lowers serum uric acid levels in gout patients, showing promise as a safe and tolerable treatment option.

New findings reveal how dysfunctional metacognitions and anger rumination contribute to pain intensity in fibromyalgia, suggesting innovative therapeutic approaches.
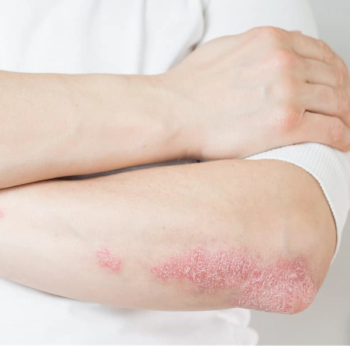
Intensive DMARD treatments significantly reduce pain in rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis, shifting focus from opioids to effective pain management strategies.

AI revolutionizes systemic sclerosis diagnosis, enhancing treatment tracking and potentially improving patient outcomes through innovative deep neural network analysis.

New findings reveal that psoriatic arthritis symptoms often appear before psoriasis, challenging traditional beliefs about their development sequence.

New research reveals that higher protein intake may enhance lean and bone mass in individuals with rheumatic diseases, suggesting a need for dietary adjustments.
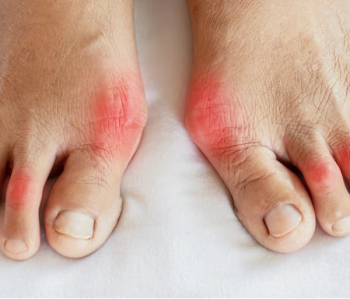
New research highlights Lipid Accumulation Product as a key predictor for gout and hyperuricemia, offering a modifiable risk factor for prevention.

An audio recap of the top 5 stories in healthcare news from the week of 05/12-05/18.

Celltrion's Yuflyma gains FDA interchangeability, offering a cost-effective biosimilar option for various conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis.

Researchers introduce the Fibromyalgia Quality of Life Scale (FM-QoLS), a reliable tool designed to assess the unique quality of life challenges faced by fibromyalgia patients.

A new study reveals semaglutide's protective effects against osteoporosis and gout in obese individuals with type 2 diabetes, enhancing metabolic health insights.

Notably, nearly 1/3 of study participants used opioids over a 12-month follow-up period, indicating significant pain.

EMD Serono previously announced that its CLE cohort had met its primary endpoint while its SLE cohort failed to follow suit.