
Varying practitioner beliefs about what makes patients who have fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) “behave” differently from the general population are complicated by a paucity of studies, heterogeneity of the patient population, and other factors.

Varying practitioner beliefs about what makes patients who have fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS) “behave” differently from the general population are complicated by a paucity of studies, heterogeneity of the patient population, and other factors.

Scheduling, event, exhibit hall, CME, and other information for attendees of the 48th Annual Meeting of the Infectious Diseases Society of America.

Despite claims that biologics for treating rheumatoid arthritis are highly effective, Medicaid patients seem to demonstrate low adherence.

Gout is the most common inflammatory arthritis. Arthrocentesis and identification of negatively birefringent monosodium urate crystals from aspirate is the gold standard for diagnosis.

With the rising incidence of obesity and an increasing older population, the burden of osteoarthritis (OA) is expected to grow. Understanding of the disease is limited, and there are indications that many patients are receiving suboptimal care.

The significant changes in the way rheumatoid arthritis has been managed include earlier, more aggressive treatment with combination therapy.

Diverse mechanisms of pathogenesis have been proposed for the autoimmune diseases. A growing body of medical literature suggests a potential effect of occupational exposures on their development.

European Union okays Vimovo for osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis

Hip injuries are common in dancers, runners, and soccer players. Knowledge of the mechanism of injury and the sport can help uncover the diagnosis. Muscular strength testing should be performed on the cardinal movements of the hip joint.

Study reveals pain diary increases perception of pain severity.

A phase II clinical study began for Galapagos NV's drug candidate GLPG0259, a novel drug being developed for rheumatoid arthritis.

A second biologic option is now available for patients in New Zealand with forms of arthritis.

Certain genetic variants were discovered that lead to arthritis in women taking aromatase inhibitors.

Purple carrots have 28 times the anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant levels of the orange carrot.

Dissimilar pharmacokinetics make blood and urine testing useful for different purposes in compliance monitoring.

Paul J. Christo, MD provides an overview of the prevalence of pain in older adults while discussing physiological age-associated changes in pain processing.

Rebecca Curtis, ACC, discussed the stages of change associated with transforming helpless patients to empowered survivors.

There are many conscious and unconscious factors that affect clinicians' reactions to patients suffering with pain.

Philip Getson, DO, takes an in-depth look at a condition that is as difficult to treat as it is to diagnose, tackling many myths about CRPS along the way.

The grief and experience of loss felt by many patients is an often overlooked component of chronic pain.

Besides the immediate impact of improperly treated pain, children can experience long-Lasting consequences.

Synovial inflammation in osteoarthritis (OA) is secondary to mechanical damage to the articular cartilage and bone. OA often is said to be a disease of weight-bearing joints, but it is more appropriate to consider them as load-bearing joints. OA is the failure of an organ, the synovial joint.

Mary Lynn McPherson gave attendees some poignant reminders about methadone treatment in a lively, entertaining, and informative session.

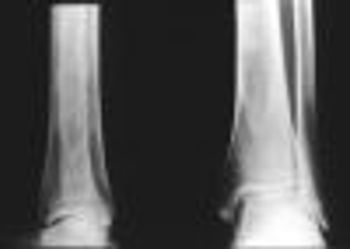
Physicians who treat athletes with traumatic foot and ankle injuries should know when to order special imaging studies, determine whether injuries can be managed in the office or require referral, and return the athlete to sports activity quickly. For simple ankle sprains, plain x-ray films usually are not indicated; functional rehabilitation is a first-line treatment.

Hepatitis C–related arthropathy is one of the most common extrahepatic manifestations of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Although symptoms can be disabling, the prognosis typically is benign. Patients who have atypical chronic inflammatory arthritis with an unknown cause should be evaluated for HCV infection.

Melanie Thernstrom, Author of

The researchers used animal models with torn ACLs to test 3 types of fluids that could be injected into the joints to serve as a substitute for lost synovial fluid: human synoviocyte lubricin that was created in a culture and then purified to be

There may be genetic susceptibility factors for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) that act only in men. In about 1% of families with SLE, all the patients with SLE are male and the women universally have positive antinuclear antibodies; also, men with SLE have more children with SLE than do women with SLE.

Do's and Don'ts of Arthritis
The standard DAS 28 score is the factor most strongly affecting the level of rheumatoid arthritis-related disability, according to a study in the Journal of Clinical Rheumatology.