
New late-breaking data from ACR 2021 show the mRNA vaccine may differ in patients dependent on their disease.

New late-breaking data from ACR 2021 show the mRNA vaccine may differ in patients dependent on their disease.

Patients who are treated with B cell depletion therapies show that their B cell count at time of vaccination can impact their COVID-19 antibody response.
Investigators observed stark contrasts in COVID-19 mRNA vaccination response among inflammatory rheumatic disease patients and the general population.

An assessment of a rheumatic disease cohort shows Spike protein antibody response is significantly decreased in vaccinated patients, and may vary by treatment.

Patients are increasingly encouraged to take an active role in the management of their chronic conditions. How much do you know about self-management in rheumatoid arthritis?

Fetal deaths associated with the rheumatic disease have been on the decline, but increased risks persist nonetheless.
Alopecia and nausea risk may be more easily identified in patients initiating methotrexate for rheumatoid arthritis.

Kyriakos A. Kirou, MD, DSc, FACP, explains the key findings of his upcoming ACR presentation, “COVID-19 Vaccine Antibody Responses in Patients Treated with B-Cell Agents Depend on B-Cell Counts at Time of Vaccine.”

An assessment of data from the DISCOVER and VOYAGE trials show the IL-23 inhibitor provides similar safety profiles in patients with either psoriatic disease.

"The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients with disease control without other immunosuppressants and prednisone-equivalent dose of ≤5 mg/day at week 52," Aranow stated.

Interim data from a post-marketing analysis suggest a boxed label warning for the drug in 2019 may have limited high-risk patients taking the biologic therapy.

A cross-sectional analysis suggests patients with worse social risk scores are significantly more likely to be impacted by juvenile idiopathic arthritis.

More data from ACR 2021 evidences the risk of minimal response to mRNA vaccines in autoimmune disorder patients on rituximab.

The oral selective inhibitor showed significant benefit versus placebo at 2 different doses in the phase 2b trial.

A new ACR 2021 study suggests patients on the biologic may be less likely to discontinue treatment than those receiving other drug classes.

New phase 3 data show TX-102 SL from Tonix may benefit central sensitization in patients afflicted with fibromyalgia pain.

A pandemic-era study suggests rheumatology care teams can capably provide beneficial care via telemedicine to treatment-stable patients.

New ACR findings suggest patients taking the common biologic drug closely leading up to their vaccination may not have a humoral response to it.

Take 5 minutes to catch up on Rheumatology Network's highlights from the week ending November 5, 2021.
While approximately 80% of patients with rheumatic disease showed humoral immune response rates following the second dose of the COVID-19 vaccine, these numbers were significantly lower than controls.
Investigators analyzed comorbidities, such as diabetes, which has been historically associated with gout, to determine what role, if any, they played in increasing the risk of lower extremity amputation.

Vibeke Strand, MD, explores her ACR presentation, “Assessing the Relationship of Patient Global Assessment of Disease Activity and Health Related Quality of Life by SF-36 with Other Patient-Reported Outcomes in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Post Hoc Analyses of Data from Phase 3 Trials of Baricitinib.”

Niti Goel, MD, discusses her ACR Convergence presentation entitled, “Depletion of KLRG1+ T Cells in a First-in-human Clinical Trial of ABC008 in Inclusion Body Myositis (IBM).”

Jean Liew, MD, MS, discusses her upcoming ACR Convergence presentation entitled, “SARS-CoV-2 Infections Among Vaccinated Individuals with Rheumatic Disease: Results from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance Provider Registry."

Karen H. Costenbader, MD, MPH, discusses her upcoming ACR Convergence presentation entitled, “Year in Review: Clinical Rheumatology."
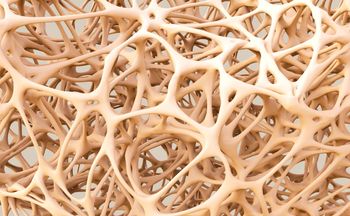
A propensity score-matched analysis comparing fracture risk associated with the initiation of SGLT2 inhibitors versus GLP-1RAs or DPP-4 inhibitors indicates use of SGLT2 inhibitors was not associated with an increase in risk of fractures in older patients with type 2 diabetes.

Take 5 minutes to catch up on Rheumatology Network's highlights from the week ending October 29, 2021.

Data show participants with early glucocorticoid use were more likely to be prescribed a biologic by 12 months, in comparison to non-users.

Cassandra Calabrese, DO, examines immunopathogenesis, immunomodulation, COVID-19 vaccinations, and pre-exposure prophylaxis.

Investigators called for the development of health care system structures to better support the exchanging of resources and information.