
Low allopurinol prescription rates and suboptimal dosing are of particular concern in adult patients in Asia with poorly controlled gout.
Connor Iapoce is the assistant managing editor for HCPLive, after joining the MJH Life Sciences team in April 2021. He graduated from The College of New Jersey with a degree in Journalism and Professional Writing. He enjoys listening to records, going to the movies, and playing with his cat, Squish. You can reach him at ciapoce@mjhlifesciences.com.

Low allopurinol prescription rates and suboptimal dosing are of particular concern in adult patients in Asia with poorly controlled gout.
The use of SGLT2 inhibitors was associated with similar or lower risks of fractures as incretin-based drugs, even in the high-risk patient population.
Most patients were able to achieve clear or almost clear skin, and improvement of arthritis and difficult-to-treat areas, with guselkumab and risankizumab treatment.

A systematic review of 11 randomized clinical trials found adults with gout exhibited similar hepatic safety profiles for both febuxostat and allopurinol treatment.

Granted to Ipsen, the breakthrough treatment reduces new, abnormal bone growth in people living with the ultra-rare bone disease.
Results from the SELECT-PsA trials indicate patients with active PsA and axial involvement demonstrated greater clinical improvement with upadacitinib 15 mg versus placebo.

Although no incidence trends were observed in a German cohort, the data indicate patients with ILD-RA have received more biological/targeted synthetic DMARDs in recent years.

The association was generally consistent across the subgroups of age, sex, use of systemic corticosteroids, and comorbidity levels in the population-based cohort.

Factors including age and disease activity influenced the selection of JAK inhibitors over biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs for RA patients beginning therapy.
A systematic review and meta-analysis of 30 studies indicates a favorable effect of TNF inhibitors on surrogate markers for CVD risk.

Each 1-SD increment in HDL-C level was associated with a 14% higher risk of fractures in cohort study of approximately 16,000 community-dwelling healthy adults.

Hydroxychloroquine dosing higher than 6 mg/kg was associated with a 15-year risk of nearly 22%, while retinopathy risk with shorter duration of use was significantly lower.

Over a 40-year follow-up, approximately one-quarter of the study cohort with juvenile arthritis were reported to have active uveitis.

Guidelines lack clear recommendations for osteoporosis management and fall prevention, which may be due to a lack of evidence in the literature.

Data show participants with early glucocorticoid use were more likely to be prescribed a biologic by 12 months, in comparison to non-users.

Data show no significant improvement in pain, function and alignment scores over 26 weeks in the PRP injection group, compared to placebo.

Data show 89 of 602 patients with rheumatoid arthritis had renal damage, with patients predominantly female and older age.
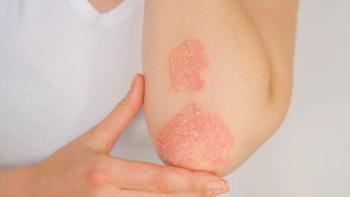
Data from the COSMOS study showed that 44.4% of patients who received guselkumab versus 19.8% of patients who received placebo achieved a ≥20% improvement at week 24.

New data show NSAIDs treatment not associated with worse in-hospital mortality rates compared to patients not treated with NSAIDs.

New data show rheumatoid arthritis and immunosuppressive treatment associated with more severe risks of COVID-19, including hospitalization and death.

A new study finds atorvastatin does not have significant effect versus placebo on treating symptomatic knee osteoarthritis, including cartilage loss.

A study finds low risk of malignancy from secukinumab treatment for psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis patients, despite limited data.

A recent study finds increasing number of women with PsA, but an overall stable incidence of disease compared to previous studies in same population.

Study participants who received combined video and booklet education were more effective in changing self-care behaviors. The education tools additionally provided greater advantages for Spanish-speaking and less-educated patients.

A new study finds educational video and booklets result in increased levels of patient knowledge in managing knee osteoarthritis, particularly among Spanish-speaking and less educated patients.